What is DevOps?
DevOps is a set of practices that combines Software Development (Dev) and IT Operations (Ops). It aims to shorten the systems development life cycle and provide continuous delivery with high software quality.
In other terms, DevOps (a portmanteau of “development” and “operations”) is the combination of practices and tools designed to increase an organization’s ability to deliver applications and services faster than traditional software development processes. This speed enables organizations to better serve their customers and compete more effectively in the market.
Importance of DevOps:
Release Velocity: DevOps practices help in increasing the release velocity. We can release code to production more often and with more confidence.
Development Cycle: With DevOps, the complete development cycle from initial design to production deployment becomes shorter.
Deployment Rollback: In DevOps, we plan for any failure in deployment rollback due to a bug in code or an issue in production. This gives confidence in releasing features without worrying about downtime for rollback.
Defect Detection: With the DevOps approach, we can catch defects much earlier than releasing them to production. It improves the quality of the software.
Recovery from Failure: In case of a failure, we can recover very fast with the DevOps process.
Collaboration: With DevOps, a collaboration between development and operations professionals increases.
Performance-oriented: With DevOps, the organization follows performance-oriented culture in which teams become more productive and more innovative.
How does DevOps work?
A DevOps team includes developers and IT operations working collaboratively throughout the product lifecycle to increase the speed and quality of software deployment. It’s a new way of working, a cultural shift, that has significant implications for teams and the organizations they work for.
DevOps teams use tools to automate and accelerate processes, which helps to increase reliability. A DevOps toolchain helps teams tackle important DevOps fundamentals including continuous integration, continuous delivery, automation, and collaboration.
The DevOps lifecycle:
Let’s learn about DevOps Lifecycle which will give you clarity on why DevOps is divided into six different phases which will give a clear idea on why DevOps:
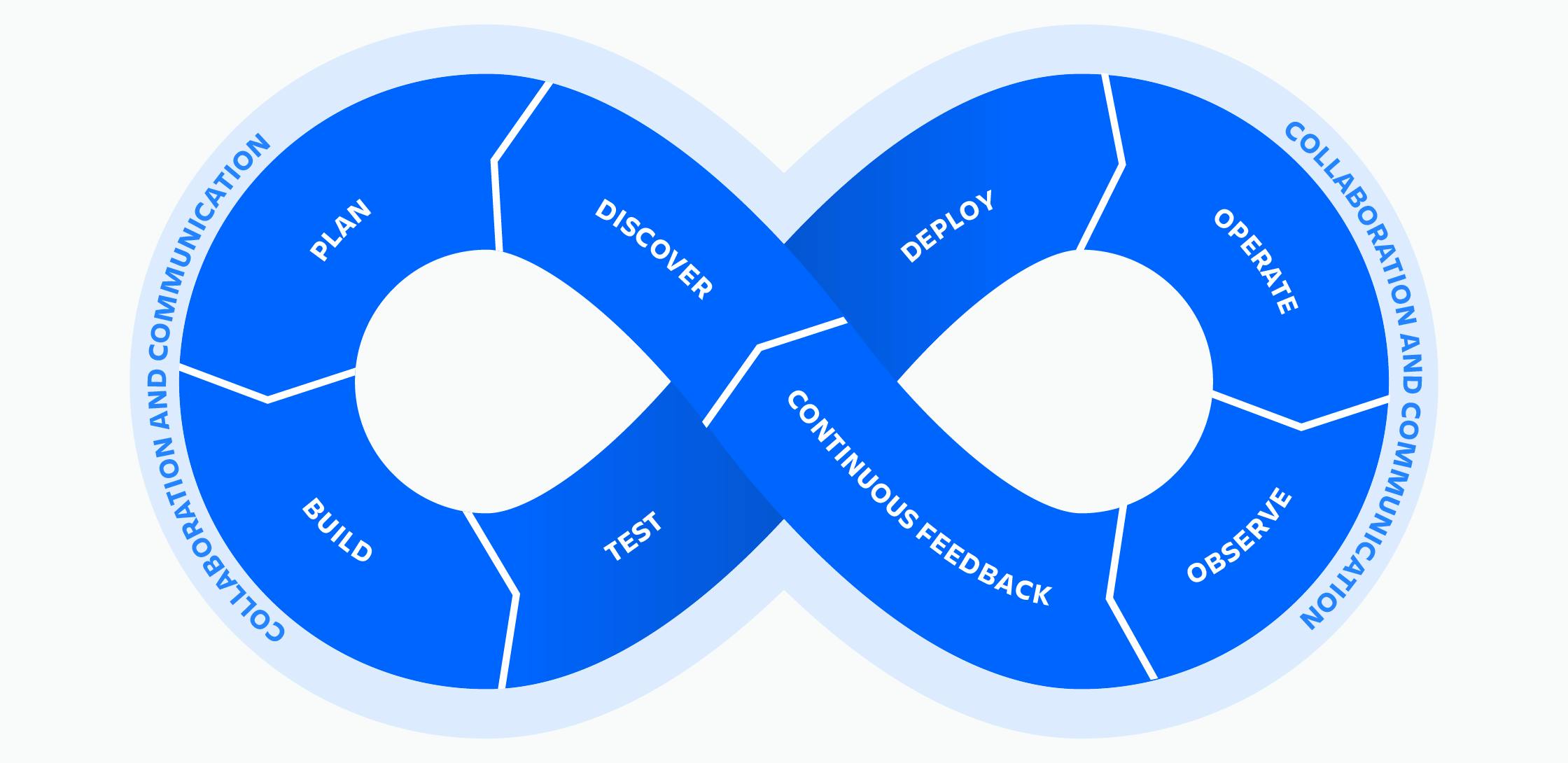
Source Code Management: In this phase, the business owners and software development team discuss project goals and create a plan. Programmers then design and code the application, using tools like Git to store the application code.
Continuous Build and Test: This phase deals with building tools, like Maven and Gradle, then taking code from different repositories and combining them to build the complete application. The application is then tested using automation testing tools, like Selenium and JUnit, to ensure software quality.
Continuous Integration: When the testing is complete, new features are integrated automatically into the existing codebase.
Continuous Deployment: Here, the application is packaged after being released and deployed from the development server to the production server. Once the software is deployed, operations teams perform tasks, such as configuring servers and provisioning them with the required resources.
Continuous Monitoring: Monitoring allows IT organizations to identify issues with specific releases and understand the impact on end-users.
Software Released: After all the phases are completed and the software meets the user’s requirement, it is released into the market.
